What is CogAT (Cognitive Abilities Test) – Gifted Assessment

CogAT, or the cognitive abilities test, is an assessment used to measure the cognitive abilities of children in grades K 12, ages 5-18. It is a standardized, aptitude test that measures a student’s ability to think and solve any given problem. It is also considered a gateway into the school’s gifted programs.
The gifted test assesses a student’s aptitude in three areas: verbal, nonverbal, and quantitative. We will discuss these 3 batteries further in the blog.
CogAT also called the gifted and talented exam is used to assess a wide range of cognitive abilities. It measures a student’s ability to understand and apply abstract concepts, solve problems, and use language to express ideas.
It can also be used to evaluate students’ ability to think critically and creatively, as well as their memory and organizational skills. It further gauges students’ ability to understand and use numbers, as well as to evaluate his/her level of knowledge in areas such as science and math.
No doubt, CogAT is an invaluable assessment to help students get into the gifted and talented program. However, it is important to note that CogAT should not be used as the sole criterion for making decisions about a student’s academic placement or educational program.
The results of this test should be used in conjunction with other factors, such as the student’s past academic performance, in order to make an informed decision.
Eligibility for CogAT test
The eligibility criteria to appear for CogAT (cognitive abilities test) vary depending on the school district or organization that administers the exam. Some school districts may require students to have a minimum qualifying score on another assessment, such as the Iowa Test of Basic Skills (ITBS) or the Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children (WISC), to be eligible for CogAT testing.
CogAT Test Pattern
The first step in CogAT exam preparation is to familiarize your child with the pattern. Make them practice the questions that are expected to come in the gifted and talented test. The Cognitive abilities test is a multiple-choice assessment that includes three batteries:
Verbal Battery
The CogAT verbal battery helps the student to develop his/her verbal cognitive abilities, such as verbal fluency, verbal reasoning, and abstract verbal concepts.
The battery is made up of three sections: practice analogies, sentence completion, and picture classification. Each section is created to assess a different ability of the student.
The practice analogies section is used to measure the student’s ability to identify relationships between pictures.
The sentence completion section helps gauge the ability to understand the verbal context and to analyze and complete sentences.
Finally, the picture classification section assists CogAT test givers to classify pictures based on the rules they are provided.
The CogAT Verbal Battery acts as a helping hand to develop verbal abilities, problem-solving skills, and confidence in the individual.
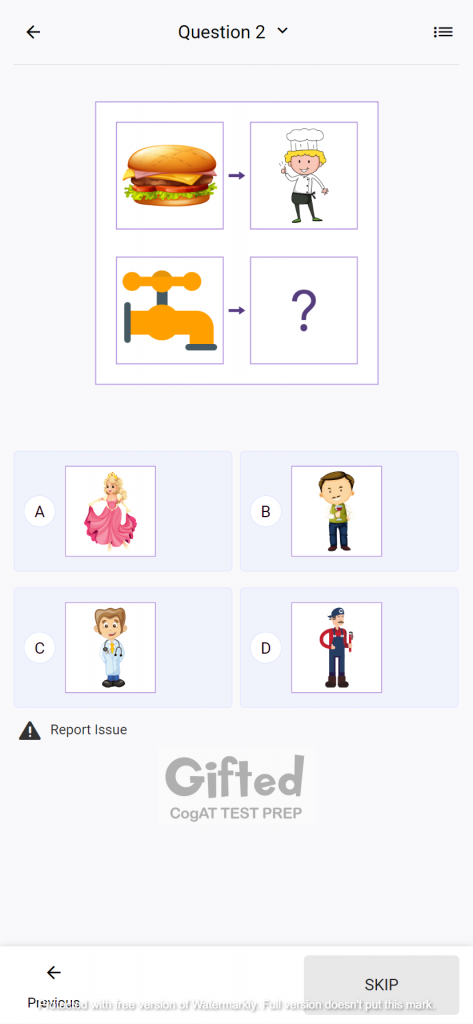
Quantitative Battery
This battery is used to determine the student’s talent to work with quantitative data and solve complex mathematical concepts. The assessment helps figure out numerical reasoning and problem-solving skills through 3 sections – number analogies, number puzzles, and number series.
Number analogies is the first part of the CogAT quantitative battery in which the student taking the test is asked to pair numbers together according to logic or comparison.
The second part is the number puzzle section in which the CogAT exam taker needs to solve number problems that involve combining smaller numbers to reach a larger number.
The last section of the quantitative battery is the number series. This test helps to compute the proficiency of the student in recognizing patterns and then using that recognition to complete a series of related number problems.
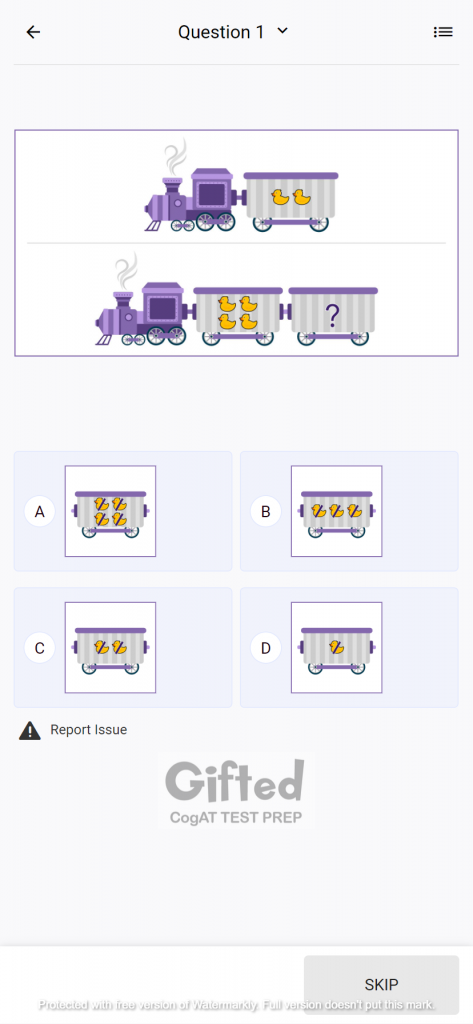
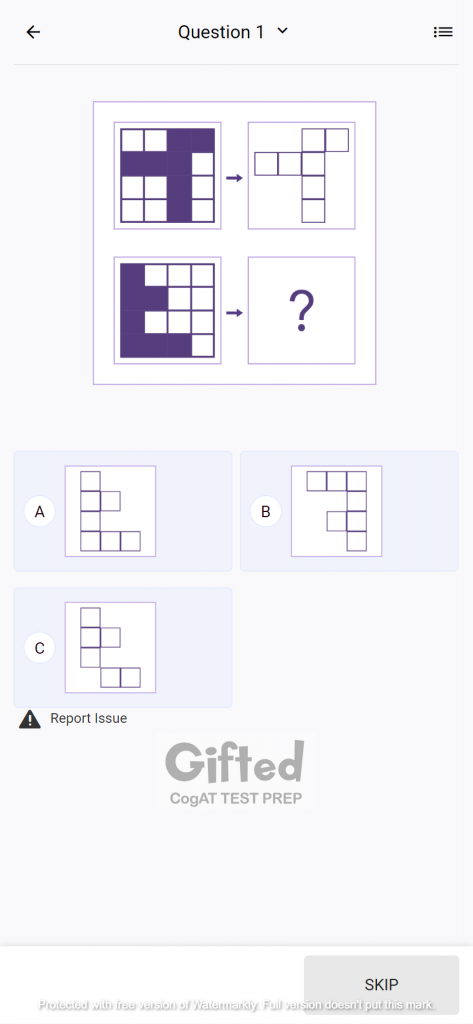
Nonverbal Battery
This battery measures nonverbal reasoning by testing figure matrices, figure classification, and paper folding. It plays a crucial role to evaluate the student’s ability to understand nonverbal cues, identify patterns, and solve problems with abstract materials.
Figure matrices is the first section that uses abstract visual problem-solving tasks to determine the schoolgoer’s ability to think flexibly while using logic to solve problems.
In the paper folding section, students are expected to predict the shapes of various paper folds based on a predetermined design. Students are expected to determine how a hole-punched, folded paper will look after it is unfolded.
The figure classification section is designed to measure a student’s ability to arrange and sort figures, symbols, and pictures into a given system or according to their characteristics. It helps to gauge their capabilities to differentiate between visual features and to recognize commonalities and differences.
Overall, these three batteries are used to determine the cognitive strengths and weaknesses of a student and to predict academic success or failure.
How is the scoring done for CogAT?
The scoring for the CogAT is based on the student’s raw score, which is determined by the number of questions answered correctly.
There is not one set score that is considered “good” as it will depend on the individual’s age group, percentile, and level of the test they took. Generally, a student scoring in the 90th percentile or higher is considered to have a good score.
Conclusion
CogAT is a complex test but with an ample amount of practice, the test can be easily cleared. The Gifted CogAT prep test app has compiled 5500+ practice questions for kindergarten to grade 5. Make your child practice a good number of questions from all three batteries to get a complete picture of his/her potential.
As parents, this will help you observe and identify the questions that your child finds difficult to understand and the time he/she takes to solve them. A well-practiced child is likely to complete the actual test with more confidence and within the stipulated time.